| Nr. | Status | Description | Figures | Further Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 | oral presentation, completed |
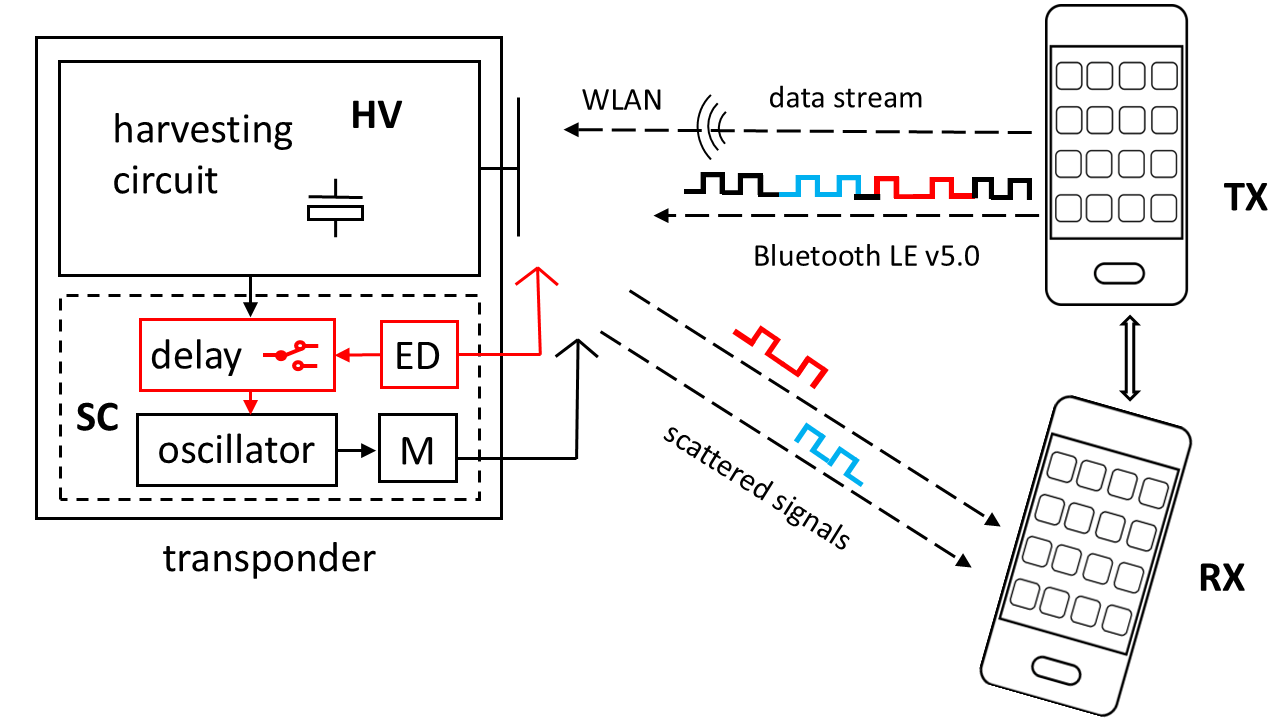
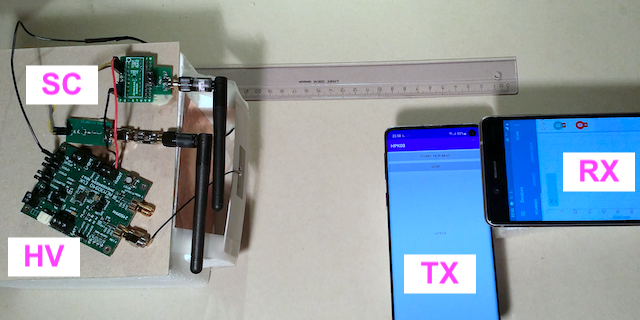
Selective Scattering Bluetooth Messages between Battery-less Transponder and Mobile Telephones This work concerns back-scattering operation of an experimental battery-less transponder operated by intentionally generated wireless signals in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. Our setup operates the transponder by using two regular mobile telephones, one for transmitting the wireless signals, the other one for receiving the back-scattered signals from the transponder. The transmitted signals consist of a power supplying data stream and specifically designed Bluetooth messages, which by themselves include different predetermined Bluetooth response messages. For the back-scattering the transponder simply selects the appropriate response messages according to the information intended for communication. This solution enables highly economical transponder operation, particularly when implemented by a SPLD (Simple Programmable Logic Device). Experiments show that this approach together with switching off subcarrier generation during waiting intervals achieves a power consumption of less than 106 μW and a wireless operational range of 8 cm, which is a 33 % improvement over our previous work. Thus, the proposed design significantly improves basic communication between a battery-less transponder and mobile telephones, which encourages further endeavors in this direction. |
|
IEEE RFID-TA Conference, Valence, France 2025 IEEE Xplore Publication |
| 27 | oral presentation, completed |
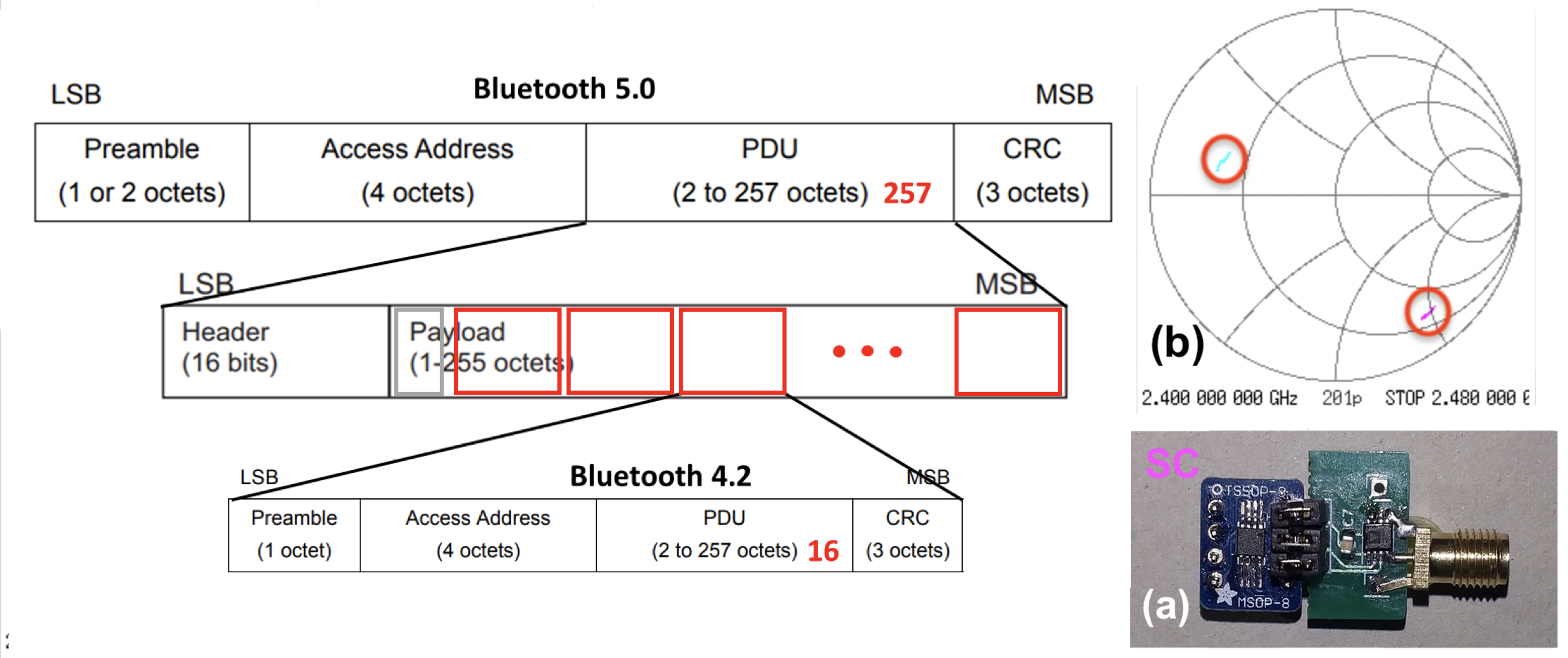
Scattering Bluetooth Messages between Battery-less Transponder and Mobile Telephones A specifically designed extended message of Bluetooth version 5.0 includes short bit sequences that serve as Bluetooth response messages detectable by a Bluetooth receiver of a mobile telephone. Experiments show that a 2 MHz frequency shifting is suitable for reducing the transponder's active power consumption to 347 μW and for achieving a wireless operational range of 6 cm. |
|
IEEE RFID-TA Conference, Daytona Beach, USA 2024 IEEE Xplore Publication |
| 25 | extended paper, completed |
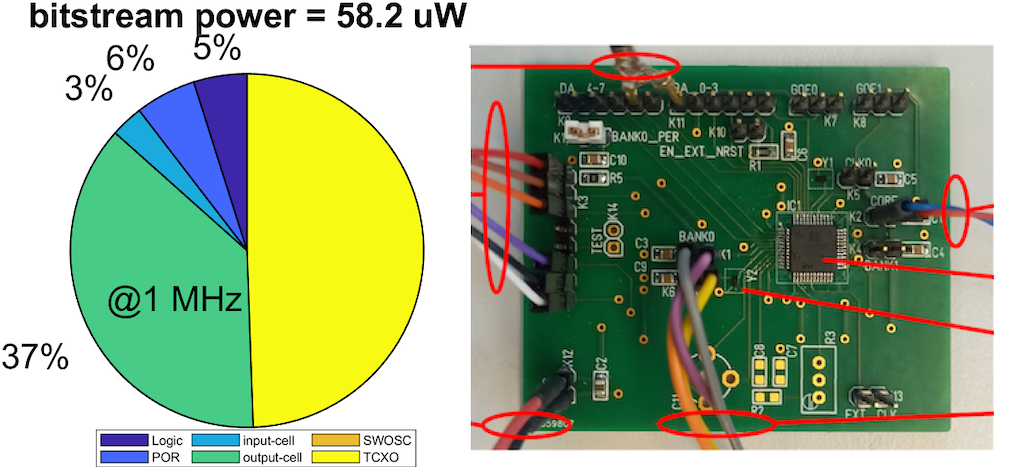
Implementations for Scattering at 1.8 Volt between Battery-less Transponder and Mobile Telephones Extended study for comparing bitstream implementation techniques: Micro Controller Unit (MCU), FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), CPLD (Complex Programmable Logic Device) and ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit). Experimental results suggest that CPLD is the most suitable for our application and demonstrate that significant power savings are achievable by transition from a fully synchronous to a low-power asynchronous implementation consuming 87 μW, a 6-fold reduction over our previous MCU setup. Research Partner: Institute for Microelectronics and Embedded Systems (IMES), Eastern Switzerland University of Applied Sciences, Rapperswil, Switzerland |
|
IEEE Journal of Radio Frequency Identification, 2024 IEEE Xplore Publication |
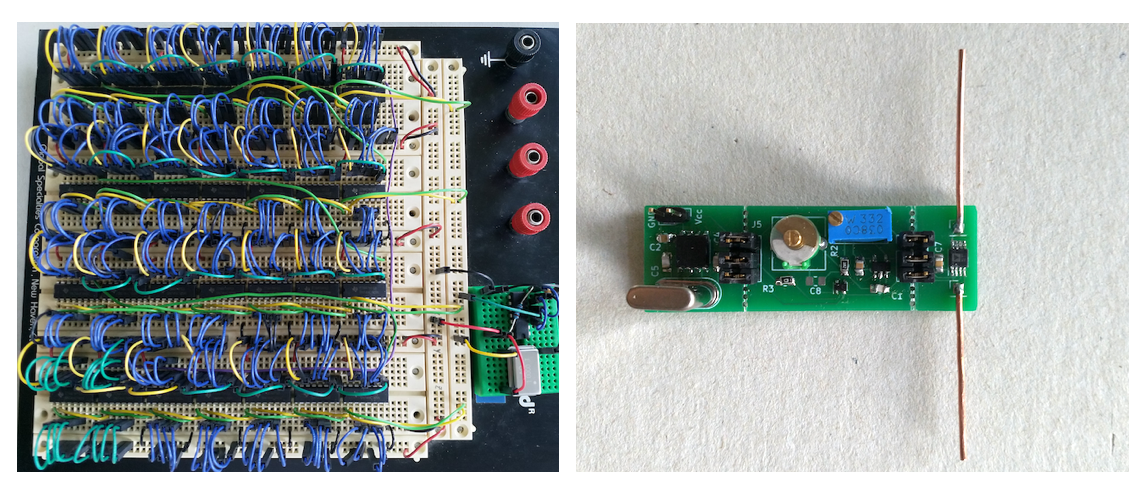
| 24 | oral presentation, completed |
RF Harvesting for Scattering at 1.8 Volt between Battery-less Transponder and Mobile Telephones
Comparison of different implementation technologies for bitstream generation and subcarrier modulation: hardware, microprocessor (MCU) as well as digital and analog designs. Experiments show that the combination of MCU and switchable analog subcarrier generator shows the most promising result with an active power consumption of less than 1.2 mW. |
|
IEEE RFID-TA Conference, Aveiro, Portugal 2023 IEEE Xplore Publication |
| 23 | project, completed |
Comparative Study Concerning Feasibility and Potential Advantages of Different Circuit Implementation Techniques The study involves relatively low-cost measures in the area of software, alternative architectures and components in the area of discrete electronics and estimations of the power consumption of an ASIC-implemention. Research Partner: Institute for Microelectronics and Embedded Systems (IMES), Eastern Switzerland University of Applied Sciences, Rapperswil, Switzerland Support: Innosuisse, Swiss Innovation Agency, Bern, Switzerland |
|
INNOSUISSE Registration |
| 21 | oral presentation, completed |
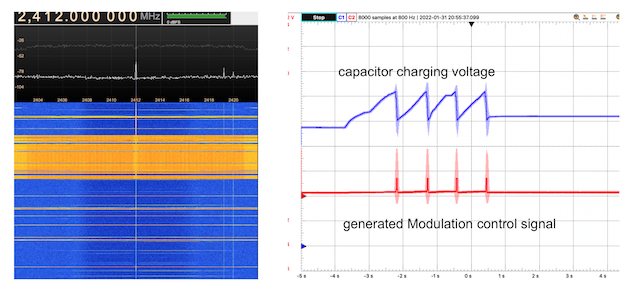
Harvesting Data Streams for Scattering between Battery-less Transponder and Mobile Telephones
WLAN signals provide a continuous data stream coexisting with BLE 5.0 advertising signals. Alternative data transfer protocols and different WLAN transmission frequencies have been studied. Results show that the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) over WLAN provides high duty cycle transmissions without interfering scattering. |
|
WPW 2022 Conference, Bordeaux, France 2022 IEEE Xplore Publication |
| 18 | oral presentation, completed |
RF Harvesting at 2.4 GHz for Scattering between Battery-less Transponder and Mobile Telephones
WLAN broadcast signals from the transmitting mobile telephone provide an additional source of energy for our battery-less transponder. An Android specific form of WLAN tethering shows the most promising potential for our scattering application based on regular, unmodified mobile telephones. |
|
IEEE RFID-TA Conference, Delhi, India, 2021 (virtual) IEEE Xplore Publication |
| 15 | oral presentation, completed |
Harvesting for Scattering Bluetooth-Signals between Battery-less Transponder and Mobile Telephones The transmitting mobile telephone sends extended Bluetooth advertizing messages and their periodic retransmissions according to the BLE version 5.0. A specifically designed code sequence generates a quasi-continuous wave signal of approx. 2 ms duration, which provides the basis for the back-scattering process. Support: Transport at Nanoscale Interfaces Laboratory of Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology |

|
Wireless Power Transfer Conference (WPTC), Seoul, South Korea, 2020 (virtual) IEEE Xplore Publication |
| 13 |
oral presentation, completed |
Harvesting for Scattering Modulated RF-Signals Receivable by Mobile Telephones A micro-controller (MCU) of a transponder is operated by using energy of RF harvesting circuit, an external 1 MHz crystal and an internal asynchronous RC oscillator for generating a frequency shift keying modulated subcarrier. The MCU consumes 9.2 mW during active operation. |
|
Conference, Wireless Power Week (WPW) London, UK, 2019 IEEE Xplore Publication |
| 10 |
poster presentation, completed |
Harvesting for Scattering RF-Signals receivable by Mobile Telephones A battery-less transponder combines RF (radio frequency) harvesting and RF scattering to modulate an incident continuous wave signal such that the scattered signal is receivable by a Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) receiver of a regular, unmodified mobile telephone. |
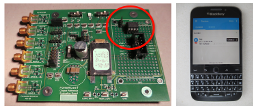 |
Wireless Power Transfer Conference (WPTC) Montreal, Canada, 2018 IEEE Xplore Publication |
| 07 |
poster presentation, completed |
Energy Harvesting in EM Fields
Evaluation of RF energy harvesting in wireless communication scenarios and implementation of harvesting circuits by designing antenna, matching circuit and voltage multiplier. The harvested energy enabled short term pocket calculator operation. Project at FHO-HSR (University of Applied Sciences), Rapperswil, Switzerland with idp invent ag as project partner |
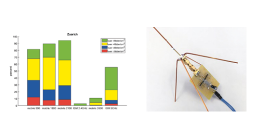 |
Project Summary Abstract |